Odoo ERP Implementation
Of many reasons to implement an ERP solution, the chief reason is the need for a common IT platform. Other reasons include a desire for process improvement, data visibility, operating cost reductions, increased responsiveness to customers and improvement in strategic decision-making.
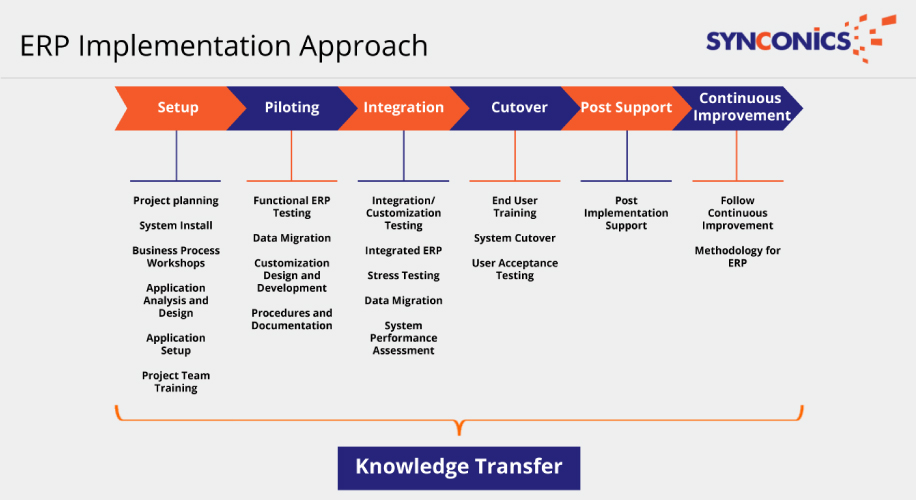
Organizations need an implementation strategy encompassing both pre implementation and implementation stages. Implementation of ERP System is a complex exercise, involving many process alterations and several legacy issues.
Following issues must be carefully thought out and formulated, as a part of implementation strategy, before embarking on actual implementation:
Business Process