Technical Foundations of ERP Architectures
ERP ARCHITECTURE
Technical Foundations of ERP Architectures basically define the layout of layers of application deployment between servers and desktops, interfaces and software objects. ERP architecture is no more meant to just provide technical functionality, user interface and platform support but should be able to absorb emerging technologies. It should be expandable and maintainable to meet future business needs such as business process changes, merger and acquisitions, compatibility with future regulations etc.
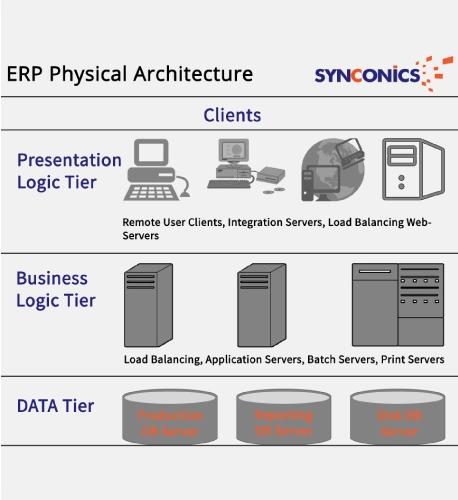
PCs (clients), networked with server/cluster of servers, are known as a Client Server platforms and have the following characteristic:
Server hosts central database and application program.
PC Clients, provide input, request service from the server, perform display, and do some processing.
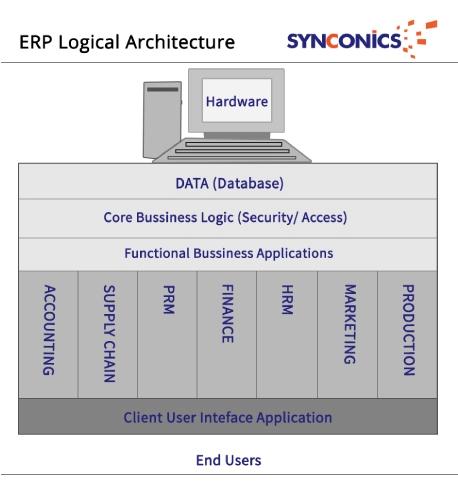
System functions are done in three logical layers